Cannabinoids: Mother Nature’s Gift of Flowers
What are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are a class of essential oils found in marijuana buds, also known as flowers. They provide psychoactive and/or physical effects when smoked, vaped, or consumed as edibles, like gummies, placed under the tongue as tinctures, or applied to the skin as lotions or balms.
Researchers have identified more than 100 hundred cannabinoids in cannabis plants. The two most bountiful and recognizable are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). THC is the cannabinoid most responsible for producing a high.
CBD makes its mark on the stoned experience by mellowing THC’s psychoactive effects.
Let’s look at the body’s system that makes these effects possible.
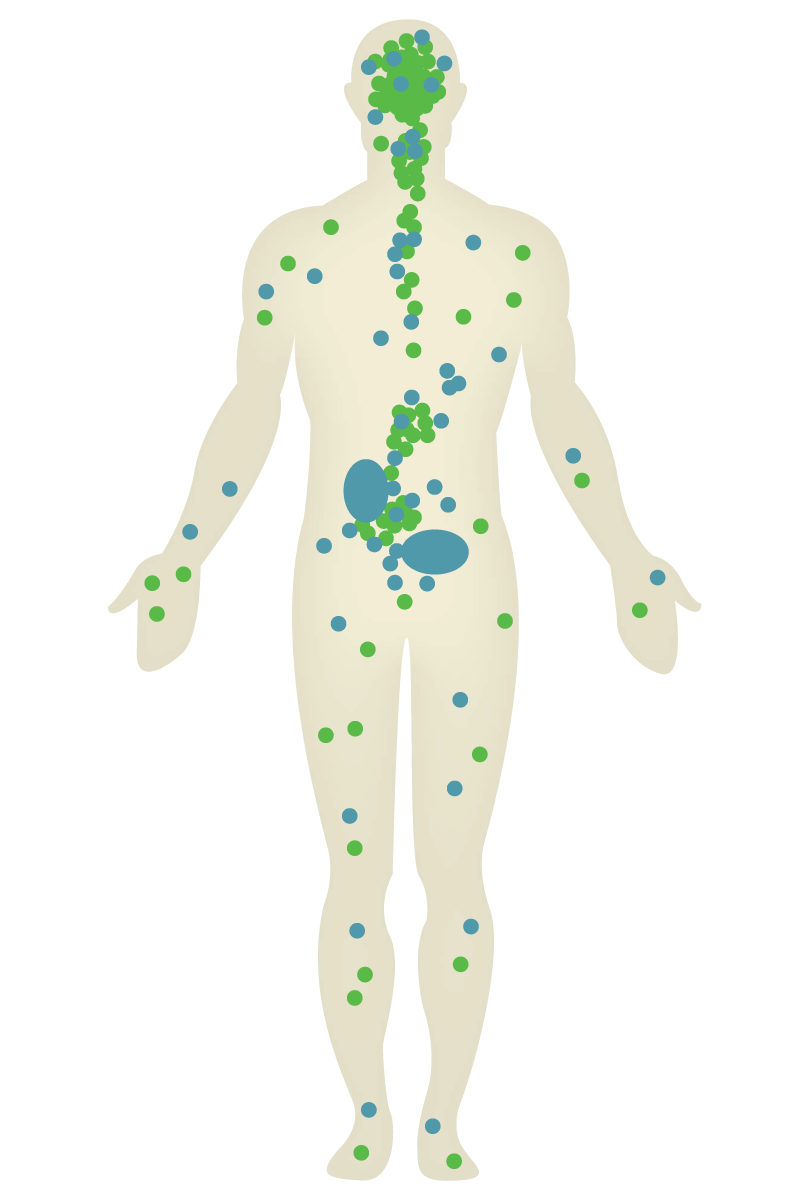
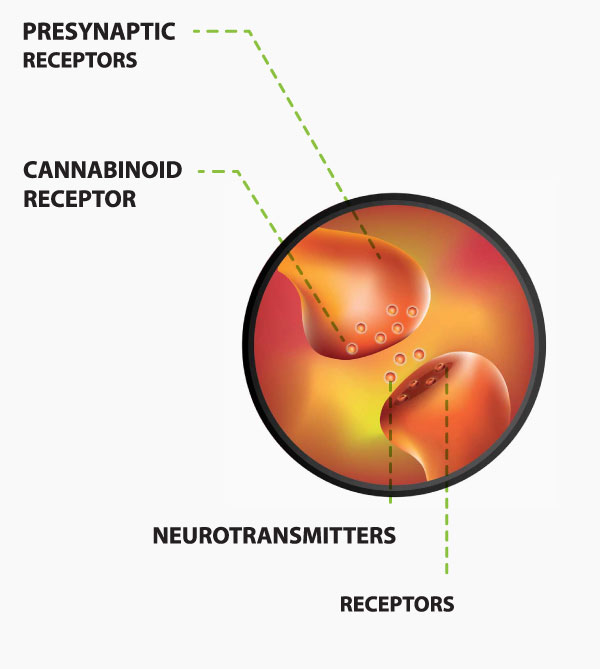
Endocannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System
Researchers “discovered” the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in the ‘90s while studying how cannabinoids affect people physically and mentally. Scientists are still working to understand the ECS. Some believe that the ECS is critical to homeostasis, the overall process in the body of stabilizing physical and brain health.
Endocannabinoids are a key component of the ECS. These molecules are strikingly similar to those in the cannabinoids found in cannabis. Like their “floral” cousins, endocannabinoids in the body bind to and interact with other essential ECS components called receptors.
C1 receptors mostly reside in the central nervous system, including the brain. C2 receptors live throughout the peripheral nervous system, including the immune system.
Receptors interacting with endocannabinoids regulate vital processes like:
- Metabolism
- Digestion
- Cardiovascular function
- Inflammation in the immune system
- Nerve system function
- Muscle and bone growth
- Motor control
- Sleep
Here are two examples:
Example 1:
You feel anxious. Interactions between C1 receptors and endocannabinoids, assuming those molecules are working properly, ease your anxiety symptoms. Dosing yourself with the cannabinoid THC creates a similar interaction. THC binds with C1 receptors to reduce your anxiety (and – voila! – get you high.)
Example 2:
You scrape your knee. A C2/endocannabinoid interaction signals your body to secrete chemicals to reduce the pain. Alternatively, you smoke marijuana, and the cannabinoid THC binds to C2 receptors, easing your pain.
These responses are a big reason why recreational pot use has been popular for millennia. It’s also why the medical community is eager to explore more deeply cannabis’s medicinal benefits.

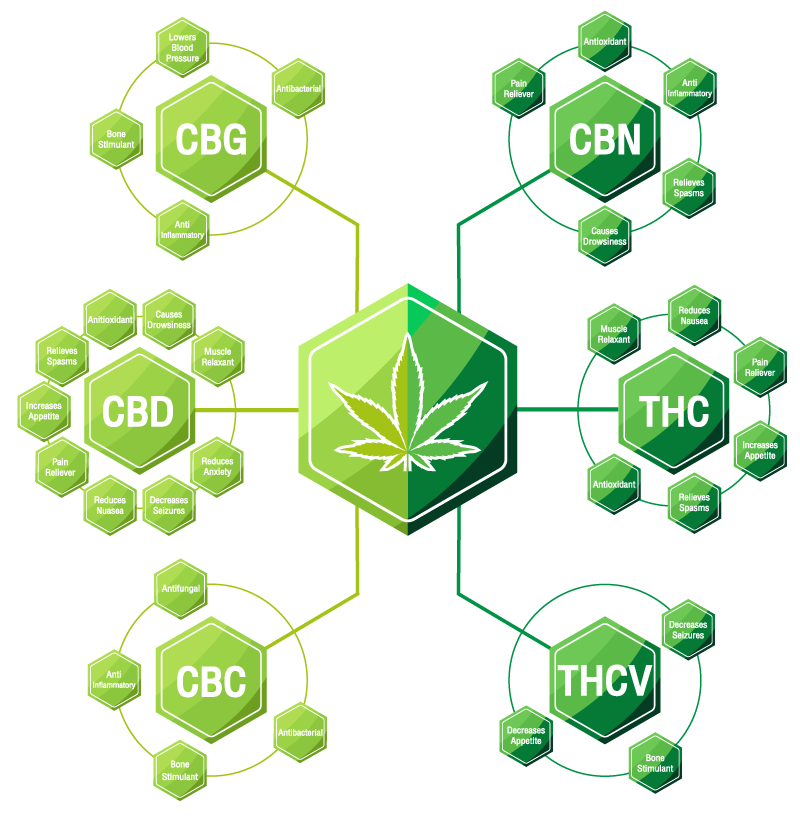
Minor Cannabinoids
Of the 100-plus cannabinoids that are not THC or CBD, four of the most noteworthy are:
Cannabinol (CBN): This cannabinoid has analgesic properties three times more powerful than aspirin. It produces minor psychoactive effects. Therapeutic properties include antibiotic, sedative, anti-convulsive, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial.
Cannabigerol (CBG:) Marijuana includes tiny amounts of CBG. Its therapeutic effects include analgesic, sedative, antibacterial, anti-fungal, and anti-tumoral.
Cannabichrome (CBC): Although it’s not psychoactive, this cannabinoid and THC interact to deepen and articulate a marijuana high. Additionally, it’s analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-depressant, and sedative.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV): Low levels of THCV heighten THC’s psychoactive effects and speed up the onset of the high.

The Entourage Effect
THC, in interaction with CBD, is mostly responsible for producing marijuana’s psychoactive effects. But a growing body of research shows THC and CBD aren’t the only influences. Distinct combinations of CBN, CBG, CBC, THCV, and other minor cannabinoids can shape the overall experience of being high.
Another key contributor to the experience is the cannabinoid category called terpenes. These essential oils are responsible for a marijuana strain’s unique flavors and aromas.
A strain’s distinct profile of THC, CBD, minor cannabinoids, and terpenes work together to create the inimitable nature of a strain’s sensory experience. In weed vocabulary, this phenomenon is called “The Entourage Effect.”